TECHNICAL INFORMATION ON EXTRUSION WELDINGHARTWIG SPITZHORN, TECHNICAL PROJECT MANAGER KWERK GMBH |
|
Components with thick walls can be, amongst others, joined together by the extrusion welding process. For PVC this procedure has only limited use and for PVDF special screws become necessary. Welding is done with wire of 3 mm resp. 4 mm and a homogenous and completely plasticized welding additive. The joint surfaces have to be warmed up and joining will be realized unter pressure. |
|
Extrusion welding is characterized by the following features: - Using of a welding additive with the same molding compound. - The welding additive is plasticized homogeneously and completely. - The surfaces to be joined are heated to welding temperature with hot air. - The extruded compound is brought into form with a welding shoe and pressed into place. Welding process: By means of the hot gas leaving the nozzle of the welding machine, the joint surfaces of the parts to be welded, are heated to welding temperature. The welding additive, continuously being extruded out of the manually operated unit, will be pressed into the welding groove. The welding pressure will be applied by means of the welding shoe, which is fixed directly to the extruder according to the welding shape. The compound stream pushes the unit forwards and regulates the welding speed. Heating up of the joint surfaces must match the welding speed. Design of the welding shoes: The extruded welding additive will be distributed with a welding shoe and then pressed into place. Welding shoes must be adapted to the particular type of seam (V-weld, fillet weld). General rule: The wider the weld seam, the longer the shoe should be. The following factors depend on the shape of the welding shoe: - Filling volume, - Injection speed, - Angle of impact, - Material flow, - Seam seal., - Uniform pressure. Temperature: Air temperature 270 – 290 ºC for PP, PE Mass temperature 230 ºC for PP, PE Air volume 350 – 400 l/min for PP, PE |
Welding seam preparation: Directly before welding the surfaces to be connected, the adjacent areas and any damaged surfaces (especially if there are weather or chemical influences) must be machined down to intact zones. This could be done in an appropriate way by means of a scraper. Cleaning agents that attack or alter the surface of the plastic must not be used. Finishing of the welding seam: Welding seams should always be made so that no subsequent machining is necessary. Extrusion welding seams should have an uniform smooth surface and flawless welded edge zones. To avoid notches in the seam root a root sealing run or seam securement can be hot-gas welded. The extrudate that occasionally oozes out at the edge of the welding shoe must – especially in the case of joints exposed to high loads – be removed manually without notches using an appropriately shaped card scraper or triangular scraper. Influence of moisture: From time to time, plastics absorb moisture, in most cases only loaded onto the surface. This moisture vaporizes during welding. The accumulated moisture can take the form of bubbles in the welding seam or in a rough surface of the seam, which can result in light loss of strength. Also humid hot gas might have this effect. Remedy: - Pre-drying of the welding additives, if possible. - Installation of a water separator in the air system. - Avoid differences in temperature between the parts being welded (condensation). |
|
Avoidance of void formation in the welded seam: Voids develop only after the welding process itself. They can be reduced by altering the level of moisture, the cooling rate and welding shoe geometry, but not by varying other welding parameters. Voids occur especially when walls are thick and/or at low working temperatures (not working temperatures). They arise because after solidification of the seam surface a stable outer skin forms which counteracts volume contraction. |
Slow and hence low-bubble cooling of the welding seam is achieved by using a covering fabric, featuring a sufficient heat resistance. This also reduces stresses and strains in the seam area. |
|
Seam types: Butt joint with V-seam  |
|
Butt joint with DV-seam 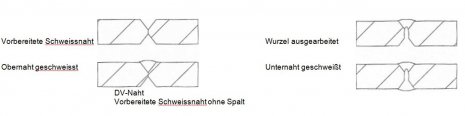 |
|
T-joint (fillet weld) with HV-seam HV – seam with fillet weld 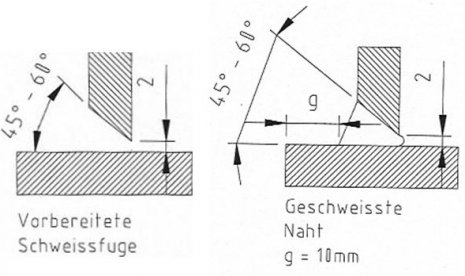 Double HV-seam Double – HV – seam with double fillet weld, prepared weld without gap 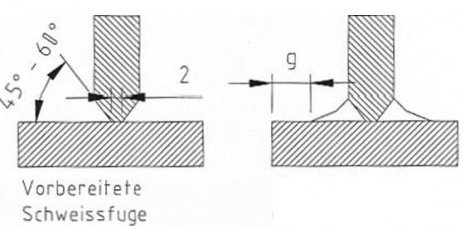 Specification of the welding shapes in the case of T-joint (fillet weld): < 20 mm wall thickness: HV-seam; material is not chamfered ≥ 20 mm wall thickness: HV-seam; material is chamfered inside the tank ≥ 40 mm wall thickness: double HV-seam; material is chamfered on both sides Factors involved enabling flawless welding seams: - Temperature of the welding additive, - Temperature of the base material, - Hot gas temperature, - Compound discharge of the extrudate, - Hot gas flow, - Welding speed, - Welding pressure. |
Optimize your shopping experience with our detailed delivery information |
Partnership at the highest level. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|











































